예방접종
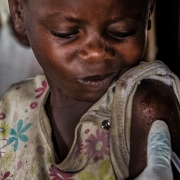
예방접종은 공중보건 영역에서 가장 비용 효율이 높은 의료적 개입 중 하나입니다. 하지만 WHO와 국경없는의사회가 권장하는 일련의 아동 예방접종으로 충분히 예방 가능한 질병들 때문에 매년 150만 명이 사망하는 것으로 추산됩니다. 현재 이 권장 예방접종으로 예방 가능한 질병은 DTP(디프테리아·파상풍·백일해), 홍역, 소아마비, B형 간염, B형 헤모필루스 인플루엔자, 폐렴구균, 로타바이러스, 결핵, 풍진, 황열, 인유두종 등입니다. 물론 모든 곳에서 모든 백신이 권장되는 것은 아닙니다.
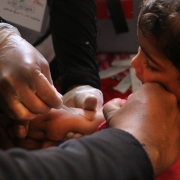
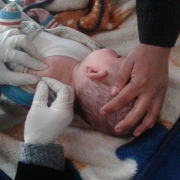
예방접종률이 대체로 낮은 국가에서 국경없는의사회는 기초 의료 지원 프로그램의 일환으로 5세 미만 아동들에게 정기 예방접종을 제공하고자 노력합니다. 예방접종은 홍역, 콜레라, 황열, 뇌수막염 등의 질병 발생에 대응하는 국경없는의사회 활동에서도 중요한 부분을 차지합니다. 대규모 예방접종 캠페인 활동에는 해당 유행병에 관한 정보, 예방접종의 유익, 예방접종과 관련된 정보(제공 단체, 시기, 장소 등)에 대해 알리는 인식제고 활동이 포함됩니다.
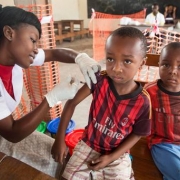
2016년, 국경없는의사회는 총 448,100회의 정기 예방접종 활동을 실시했습니다.
Vaccinations
Immunisation is one of the most costeffective medical interventions in public health. However, it is estimated that 1.5 million people die every year from diseases that are preventable by a series of vaccines recommended for children by the World Health Organization and MSF. Currently, these are DTP (diphtheria, tetanus, pertussis), measles, polio, hepatitis B, Haemophilius influenzae type b (Hib), pneumococcal conjugate, rotavirus, BCG (against tuberculosis), rubella, yellow fever, and human papillomavirus – although not all vaccines are recommended everywhere.
In countries where vaccination coverage is generally low, MSF strives to offer routine vaccinations for children under the age of five when possible as part of its basic healthcare programme. Vaccination also forms a key part of MSF’s response to outbreaks of measles, cholera, yellow fever, and meningitis. Large-scale vaccination campaigns involve awareness-raising activities regarding the epidemic disease, benefits of immunisation, as well as information in regards to who, when, and where to get the vaccine.
MSF conducted 448,100 routine vaccinations in 2016.