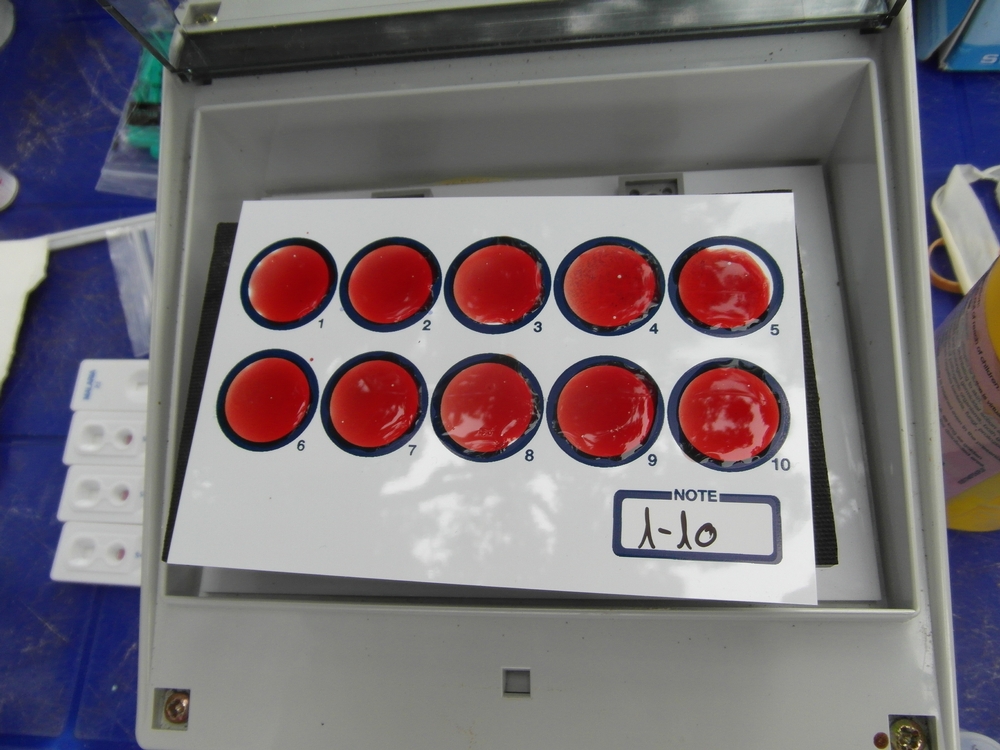
사진: 수면병 검사에 활용할 혈액 샘플. 이 병은 두 단계로 나뉜다. 1단계에서는 독성이 낮은 약으로도 치료가 가능하다. 반면 2단계에 접어들면 '니푸르티목스-에플로르니틴 병용요법'(NECT)으로 치료한다. 국경없는의사회 이동 진료팀들은 아프리카 곳곳을 다니며 수면병 진단 및 치료를 제공하고 있다. ©Philipp Frisch/MSF
수면병 (인간 아프리카 트리파노소마증)
일반적으로 ‘수면병’이라고 알려진 ‘인간 아프리카 트리파노소마증’은 사하라 이남 아프리카에서 체체파리가 옮기는 기생충병입니다. 수면병 감염 후기에 접어들면 중추 신경계가 공격받아 심각한 신경학적 장애가 나타나고, 치료를 받지 않을 경우 사망에 이를 수도 있습니다. 보고된 감염 사례의 95% 이상은 아프리카 서부·중부에서 발견되는 감비아파동편모충(Trypanosoma brucei gambiense)이라는 기생충이 유발합니다. 1999년에서 2015년 사이, 신규 감염환자로 보고된 숫자는 2만8000명에서 2800명으로, 무려 90%나 줄어들었습니다.
수면병은 감염 초기에는 비교적 치료가 쉽지만 진단이 어렵습니다. 고열, 무기력 같은 증상은 다른 여러 병에 걸렸을 때도 나타나는 증상이기 때문입니다. 감염 2단계가 시작되면 기생충이 중추 신경계에 침입해 협응(원활한 근육 운동) 저하, 혼란, 경련, 수면 수면 장애 등의 신경학적 혹은 정신적 증상이 나타납니다. 정확한 진단을 위해서는 척수액 검사 등 총 3가지 검사를 실시해야 합니다.
국경없는의사회, 소외질병 치료제 개발기관(Drugs for Neglected Diseases Initiative, DNDi), 전염성 질환 전문센터(Epicentre) 등이 함께 개발한 ‘니푸르티목스-에플로르니틴 병용요법’(Nifurtimox–Eflornithine Combination Therapy, NECT)은 현재 세계보건기구(WHO)가 권장하는 프로토콜입니다.
NECT는 비소를 함유하고 있는 기존 치료제 멜라소프롤을 사용하는 것보다 훨씬 안전합니다. 현재 DNDi에서 개발 중인 신약 펙시니다졸이 대규모 임상시험 단계를 거치고 있는데요. 이 약이 모든 검증 단계를 마치고 나면 수면병 감염의 어느 단계에서든 경구 처방이 가능한 안전하고 효과적이며 신속한 치료가 가능해질 것으로 기대됩니다.
2016년, 국경없는의사회는 수면병 환자 150명을 치료했습니다.
Sleeping sickness (human African trypanosomiasis)
Generally known as sleeping sickness, human African trypanosomiasis is a parasitic infection transmitted by tsetse flies that occurs in Sub-Saharan Africa. In its latter stage, it attacks the central nervous system, causing severe neurological disorders and death if left untreated. More than 95 per cent of reported cases are caused by the parasite Trypanosoma brucei gambiense, which is found in western and central Africa. The reported number of new cases fell by 90 per cent between 1999 and 2015 (from around 28,000 to 2,800).
During the first stage, the disease is relatively easy to treat but difficult to diagnose, as symptoms such as fever and weakness are non-specific. The second stage begins when the parasite invades the central nervous system and the infected person begins to show neurological or psychiatric symptoms, such as poor coordination, confusion, convulsions and sleep disturbance. Accurate diagnosis of the illness requires three different laboratory tests, including a sample of spinal fluid.
Nifurtimox-eflornithine combination therapy or NECT, developed by MSF, Drugs for Neglected Diseases initiative (DNDi) and Epicentre, is now the World Health Organization-recommended protocol.
NECT is much safer than melarsoprol, the drug that was previously used to treat the disease, and which is a derivative of arsenic. A new drug being developed by DNDi, fexinidazole, is currently in late-stage clinical trials and once approved will hopefully lead to a safe, effective, short-course treatment for both stages of the disease that can be administered orally.
MSF treated 150 people for sleeping sickness in 2016.